- Home
- Profile
- Tech ⤥
- Core
- Foundation ⤥
- Sprint 1 ⤥⤥
- Sprint 2 ⤥⤥
- Sprint 3 ⤥⤥
- Sprint 4 ⤥⤥
- Sprint 5 ⤥⤥
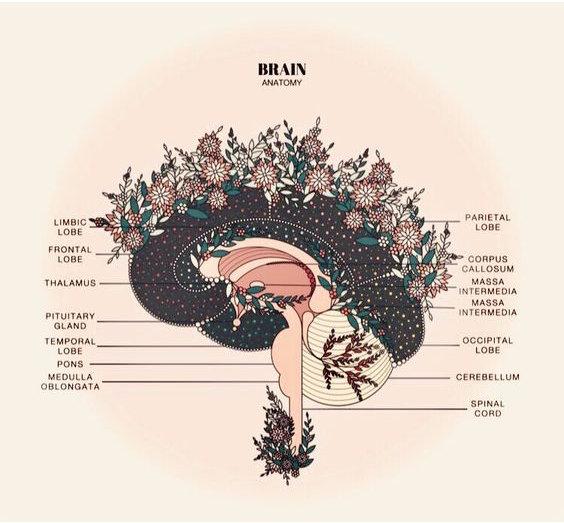
Neuroplasticity
What Is Neuroplasticity?
The fluid change of brain cells and brain regions is called neuroplasticity. Previously, it was said that brain cells such as neurons stabilize when the brain stops growing, but recent research has shown that brain cells continue to grow or decline depending on learning or various environments. Old neurons decline and new neurons appear, showing very active brain plasticity.
How Does Neuroplasticity Relate With Our Learning Behaviours?
It has been discoverd that neuroplasticity has properties that can change biological, chemical and physical
characteristics.
But as the brain changes, functions and behaviours are modified in a parallel process. New learning is a key
concept of plasticity, and the brain learns anew by making good use of a new environment.
New learning can happen anywhere, anytime, in any form. For example, children learn large amounts of new
knowledge, and their brains work especially intensively to take in new knowledge at an early age.
New learning is driven by individual needs and thirst for knowledge. The variety of situations for new learning
opportunities activates the brain to ask new questions every time you learn something.
It appears that the potential for platicity is realised when the brain acquires new knowledge and the learned
behavour functions appropriately.
Changing the brain into a shape suitable for learning requires behavioural change. In other words, it requires
association with the newly learned behaviour. New learning changes the brain by integrating organisms and
behavours.
More importantly, learning experiences bring greater compensation.
What Can Elicit Neuroplasticity?
What is the big difference between the human brain and a computer?
The point is that computers stop at just accepting and sending out information, but the brain constantly changes
according to people's thoughts and actions.
Neuronal circuits in the brain are structurally and functionally reorganised by external stimulation,
experiences and learning.
The theory of neuroplasticity supports this case by explaining that our brains have been evolved the ability to
reengineer themselves in response to experiences.
These brain changes also appear in psychological experiences. If we repeat negative thoughts such as worry and
anxiety, our brain nerves develop to increase those thought.
Conversely, if you can continue to think positive thoughts such as love and gratitude, the brain nerves that
feel happiness increase.
According to the speach 'The Plasticity of the Brain' spoken by Dalai Lama in 2005 at the regular academic
conference of the Society for Neurosicence,
brain changes happen when people engage in meditation. He especially emphasized loving-kindness meditation, and
said that when you reach the middle of loving-kindness meditation, you can feel a flood of emotions such as
love, peace, and compassion.
It has been researched that Tibetan monks have the function of the left prefrontal lobe was dominant. The left
prefrontal lobe is in charge of the optimistic and active brain, that is, the role of feeling happy.
The outcomes of these examples suggest that we can create a 'happy brain' by ourselves through meditation by
maintaining positive thoughts in our brains to change brain into optimal condition.
It is not limited to meditation only to elicit neuroplasticity however it can be happen from various ways like
being passionately engaged to new learning environment to vigorously activate the brain changes.
Useful References
1. Call, M. (2019, August 8). Neuroplasticity: How to Use Your Brain’s Malleability to Improve Your
Well-being.
Accelerate.
https://accelerate.uofuhealth.utah.edu/resilience/neuroplasticity-how-to-use-your-brain-s-malleability-to-improve-your-well-being
2. Water, S. (2021, September 29). What is neuroplasticity? The power to change your mind. BetterUp.
https://www.betterup.com/blog/what-is-neuroplasticity
Growth Mindset
What Are Growth Mindset/Fixed Mindset?
Growth mindset is a concept writte by Dr Carol Dweck, psychological professor at Stanford University, in her
book named 'Mindset: New Psychology of Success'. This concept includes:
- Persontal growth through dedication and hard work, not limited to natural talent
- Self love of learning
- People with personal resilience for greater achievement
- Members with a growth mindset motivate themselves within the organisation, innovate processes, and improve
productivity and performance
The opposite of a growth mindset is the concept of a fixed mindset.
People with a fixed mindset are charaterised by:
- Talent and intelligence are innate
- People are limited to what they can improve
- Good things and bad things are determined by one's limitations
- Avoid challenges and give up easily
- Tend to ignore or reject negative feedback about oneself

How Are They Relevant To Us?
A growth mindset is not a fixed mindset in which the future is immutable and nothing will change no matter how
hard one tries. Many studies prove that people with a growth mindset have higher satisfaction and performance in
academics and organizations.
When applying the Dweck's concept into the perspective of duty, fixed mindset is that one cannot be changed by
the duties as they are given from external environment. Contrarily, growth mindset is a mindset in which one
sees to able to change the duty on own initiative.
It is important to have a growth mindset, which is not a fixed mindset that views work as determined by the team
or organisation, but a belief that one can take the lead in work and proactively change work. It is first
compulsory requirement in many environments where you can work as a team.
As a result, members with a growth mindset can build trust-based performance expectations and relationships with
team leaders, facilitate collaboration with team members, and facilitate information sharing and communication.
Furthermore, it is possible to prevent a virtuous cycle structure in which the organisation performs its work in
a healthy manner despite changes in the internal and external environment, has a positive effect on the overall
performance of the organisation, and establishes itself as a key internal talent.

Personal Integration of Growth Mindset Into My Journey
First of all, I have felt many things while researching this topic. Personally, I think I have had a fixed
mindset, trying to give up easily when faced with difficulties came up and putting unneccesary effort into
insufficient conditions and wrong points while people with growth mindset put their effort into professional
course.
I have come to realise that this growth midset is very crucial to whatever work I will do in future and to my
mental health.
If I learn a growth mindset and integrate it fully to myself, then I will be able to embrace challenges, face
and perservere in whatever obstacles come my way, and ultimately achieve the highest level of achievement.
Currently, I seemingly have a mixed mindset, but I plan to continue to change and improve with future
experiences and efforts to be closer to having growth mindset. And in the future,including this bootcamp, I will
continue to see physical and mental limitations, but it is not that I will not acknowledge the limitations, but
I will not prevent myself from achieving better results by acknowledging the limitations in advance.
Useful References
1. Sutton, J., Ph.D. (2021, October 27). 18 Best Growth Mindset Activities, Worksheets, and Questions.
Positive Psychology.
https://positivepsychology.com/growth-mindset/